准备看点Coursera
- week 3
- 2-d-quadrotor-control
- state-space form[状态空间]
- Identify the order, n, of the system
- Define the states, $x=y(t), x_1 = \dot y(t) \dotsc$
- Create the states vector, $\mathbf{x} = [x_1, x_2, \dotsc ]^T = [y, \dot y, \dotsc ]^T$
- write system of first-order differencial equations as matrix.
-
$$
\begin{bmatrix}
\dot x_1\\
\dot x_2\\
\dotsc\\
\dot x_n
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
x_2\\
x_3\\
\dotsc\\
g(x_1, x_2, \dotsc, x_n, \mathbf{u})
\end{bmatrix}
$$
- $\mathbf{\dot x} = f(\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{u})$
- example 1[Mass-Spring System]
- example 2[Planar Quadrotor Model]
- Define states $x_1 = y,x_2 = z, x_3 = \phi, x_4 = \dot y, x_5 = \dot z, x_6 = \dot \phi$
-
$$
\begin{aligned}
m\ddot y &= sin(\phi) u_1\\
m\ddot z &= cos(\phi) u_1 + mg\\
I_{xx} \ddot \phi &= u_2
\end{aligned}
$$
-
$$
\begin{bmatrix}
\dot x_1\\
\dot x_2\\
\dot x_3\\
\dot x_4\\
\dot x_5\\
\dot x_6\\
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
x_4\\
x_5\\
x_6\\
\frac{\sin(x_3)u_1}{m}\\
\frac{\cos(x_3)u_1}{m} - g\\
u_2
\end{bmatrix}
$$
- Linearization
- For PID controller, it is designed for a linear system
- So, we need linearize equation of motions.
- For 2D Quadrotor Control
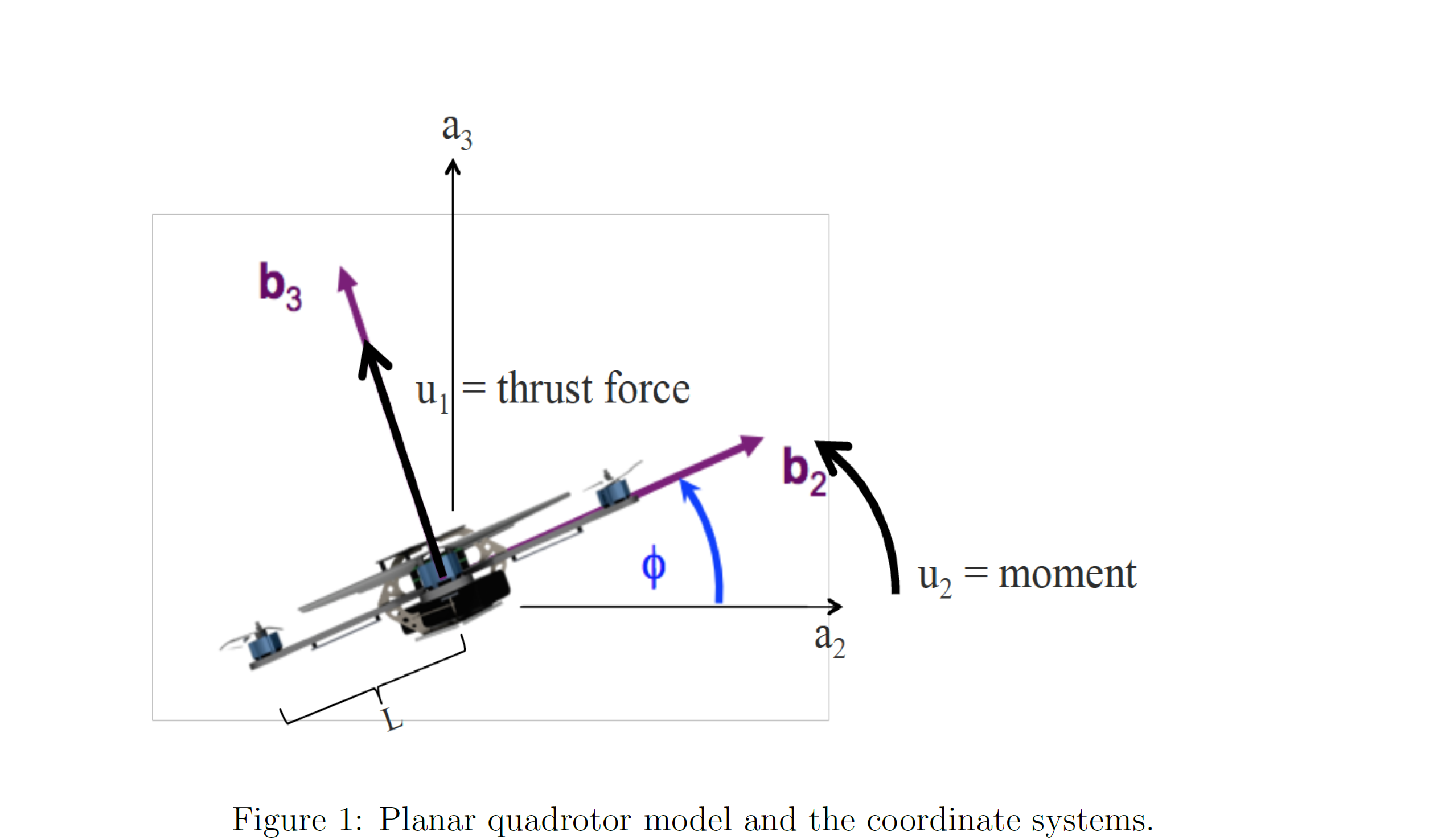
- Rotation matrix
- $\begin{bmatrix}\cos\phi& -\sin\phi\\sin\phi&\cos\phi \end{bmatrix}$
- $u_1=F_1 +F_2$
- $u_2 = L(F_1 - F_2)$
- L is the arm length of the quadrotor.
- Newton equation
- Euler equation
- Newton-Euler equation
- $\begin{bmatrix}\ddot y\\ddot z\\ddot\phi\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}0\-g\0\end{bmatrix} + \begin{bmatrix}
-\frac{1}{m}\sin\phi&0
\frac{1}{m}\cos\phi&0
0&\frac{1}{I_{xx}}
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
u_1\u_2
\end{bmatrix}
$
- Linearization
- PD controller
-
$$
\begin{aligned}e_p&=r_T(t)-r\\e_v&=\dot r_T(t) - \dot r\end{aligned}
$$
- $\ddot r_c=\ddot r_T(t) + k_pe_p+k_ve_v$
-
$$
\begin{aligned}
u_1&=mg+m\ddot z_c&=&m[g+\ddot z_T(t)+k_{vz}(\dot z_T(t) - \dot z) + k_{pz}(z_T(t)-z)]\\
u_2&=I_{xx}\ddot \phi_c &=& I_{xx}[\ddot \phi_T(t)+ k_{v\phi}(\dot\phi_T(t) - \dot\phi) + k_{pz}(\phi_T(t) - \phi)]\\
\phi_c &= -\frac{\ddot y_c}{g} &=& -\frac{1}{g}[\ddot y_T(t) + k_{vy}(\dot y_T(t) - \dot y) + k_{py}(y_T(t)-y)]
\end{aligned}
$$
- // TODO
- Not totally figure out what is the relationship between
states-space form and the PD controller
- Trajectores[轨迹追踪]
- Target
- Start, goal positions
- Waypoint positions
- Smoothness criterion
- Order of the system(n) [系统阶数]
- n=1, 指定任意速度, velocity
- n=2, 指定任意加速度, acceleration
- n=3, 指定任意加加速度, jerk
- n=4, 指定任意加加加速度, snap
- Calculus of variations[变分法]
- Euler-Lagrange Equation[欧拉拉格朗日方程]
- $\frac{d}{dt}(\frac{\partial\mathcal L}{\partial\dot x}) - \frac{\partial \mathcal L}{\partial x} = 0$
- for $\underset{x(t)}{\argmin} = \int_0^T{\dot x^2}dt$
- 速度最小时的方程
- $\mathcal{L}(\dot x,x, t) = \dot x^2$
- Solution(匀速直线运动)
- $x(t) = c_0t + c_1$
- for $\underset{x(t)}{\argmin} = \int_0^T{\sqrt{1+\dot x^2}dt}$
- hence $ds = \sqrt{1+\dot x^2}dt$
- $\mathcal{L}(\dot x,x, t) = \sqrt{1+\dot x^2}$
- 找到A点到B点的最优曲线(速度最小)
- Solution(匀速直线运动)
- $\dot x(t) = \sqrt{\frac{K}{1-K^2}} = c_1$
- $x(t) = c_1t+c_0$
- for $\underset{x(t)}{\argmin}\int_0^T(x^{(3)})^2dt$
- $\mathcal{L}(x^{3}, \ddot x, \dot x, x, t) = (x^{(3)})^2$
- $\frac{\partial\mathcal{L}}{\partial x} - \frac{d}{dt}(\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}}{\partial \dot x}) + \frac{d^2}{dt^2}(\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}}{\partial \ddot x}) - \frac{d^3}{dt^3}(\frac{\partial \mathcal{L}}{\partial x^{(3)}}) = 0$
- Finish
- week 4
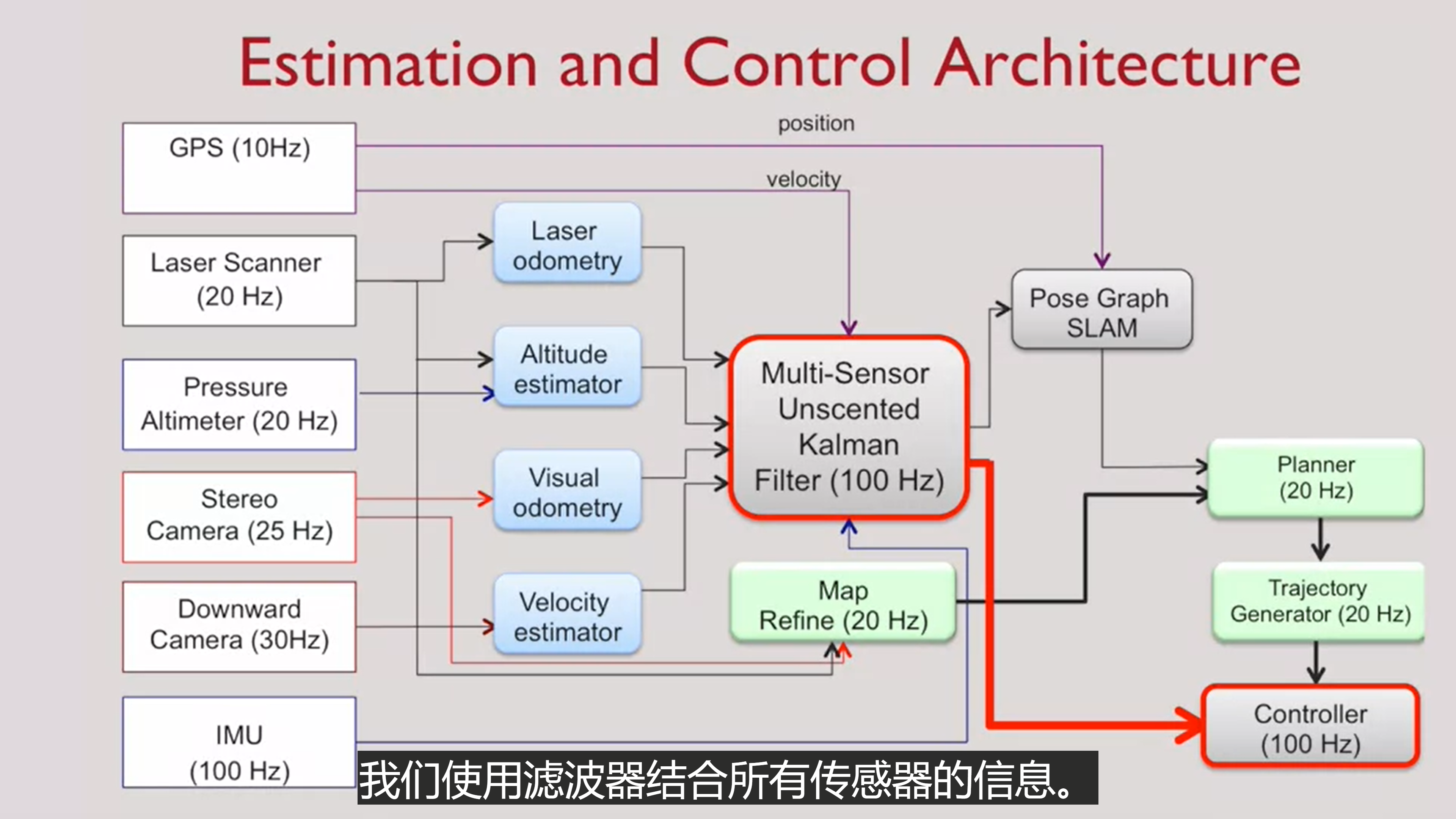
- Estimation and Control Architecture
- Finish
- This course is too complex
准备看公众号
- 基于RGB-D相机的三维重建总览[基于fusion系列的三维重建]
- 静态场景
- KinectFusion✔
- Kintinuous
- ElasticFusion
- ElasticReconstruction
- InfiniTam
- BundleFusion👍
- 动态场景
- DynamicFusion✔
- Paper [Newcombe]
- 对于帧间较大的运动以及遮挡区域的运动都不具备鲁棒性
- 可以较好的处理封闭拓扑表面的重建
- 回环闭合失败
- 2015 cvpr best paper award
- volumeDeform
- BodyFusion👍
- Paper [Tao Yu]
- BodyFusion使用人体骨架作为先验信息,实现鲁棒了的人体动态重建。人体骨架的引入减少了重建表面图节点的非刚性形变参数化的歧义性,也是在一定程度上缩小了解空间。
- 关节点太过稀疏, 运动过快,存在运动模糊
- DoubleFusion👍
- Paper [Tao Yu]
- 参数化人体(SMPL[Skinned Multi-Person Linear Model])的同时增加一个outer surface, 进行联合运动追踪
- 当人体穿着肥大,估计的人体偏胖
- 无法处理外层表发生分离的情况,以及无法处理人和物体交互的情况
- UnstructuredFusion
- Paper [Lan Yu]
- 多相机系统
- 可以使用未经预先标定以及同步的三个深度相机以一种互补并灵活的方式覆盖整个人体,从而实现实时,高质量,完整的动态人体重建
- 输入深度图分辨率受限
- RobustFusion
- Paper [Zhuo Su]
- 各种数据驱动的视觉线索提高动态重建算法的鲁棒性
- Occupancy Network,Pose&Shape Network以及Semantic Network
- 无法实时运行
- 处理重建网格拓扑发生分离的情况, 脱掉衣服
- 不能实现人和物的交互
- KillingFusion
- SurfeiWarp
- Fusion4D👍
- Paper [Mingsong Dou]
- 多视角方案
- 引入了key volume
- 对于较大的帧间运动以及网格拓扑发生改变时都有很强的鲁棒性
- 体素碰撞检测
- 输入流帧率过低或者帧间运动过大时,会使帧间对应匹配点估计不准确