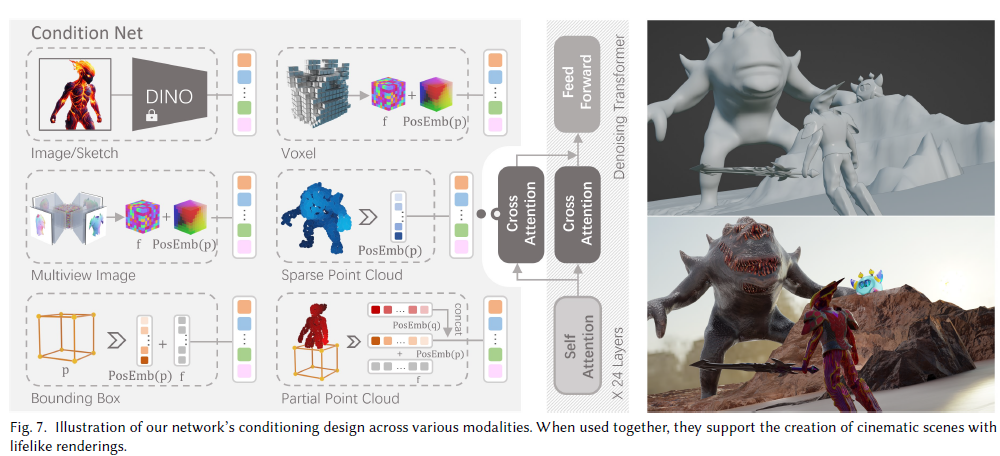
Nonlinear Least Squares [非线性最小二乘法]
- Method for non-linear least suqares problems - 2004
- Descent method
- The steepest descent method[最速下降]
- Newton’s method[牛顿下降]
- Linear Search[线性搜索]
- Trust Region and Damped Methods
- Non-linear least squares problems
- The Gauss-Newton Method
- The Levenberg-Marquardt Method
- Powell’s Dog leg Method
- A Hybrid Method: L-M and Quasi-Newton
- A Secant Version of the L-M Method
- A Secant Version of the Dog leg Method
- Final Remarks
Optical Flow Method[光流法]
- 基本假设
- 亮度恒定不变, 由于需要对比两张连续的照片计算光流场,因此,如果亮度改变的话,图像匹配会存在误差
- 时间连续,或运动范围比较小,时间连续是为了让图像间的点满足对应关系
- 同一个点发生了位移,亮度应当是不变的
- 有$I(x,y,t)=I(x+dx, y=dy, t’)$
- 泰勒展开后得到
$\begin{aligned}
I(x,y,t)&=I(x+dx, y+dy, t+dt)\\
&=I(x,y,t) + I_xdx+I_ydy+I_tdt + R(x,y,t)&\text{R为高阶余项,当做0处理}\\
0&=I_xdx+I_ydy+I_tdt
\end{aligned}$
- 其中
- $I_x, I_y, I_t$分别为光强对$x,y,t$的偏导数
- 偏导数的计算可以通过图像数据计算
- $dx, dy$为我们需要求的光流矢量,在一些教程中也会以$u,v$来表示,即$I_xu+I_yv+I_t=0$
- 为了求解$dx, dy$我们至少需要2个方程,即2个点,当点的数量超过2时,我们就需要用一些约束来求解最优解
光流法-不同的约束条件
基于梯度的方法
- 利用图像的灰度的微分来计算速度矢量
- Horn-Schunck
- Lucas-Kanade(LK)
基于匹配的方法
基于能量(频率)的方法
金字塔方法
基于相位的方法
神经动力学方法
深度学习算法
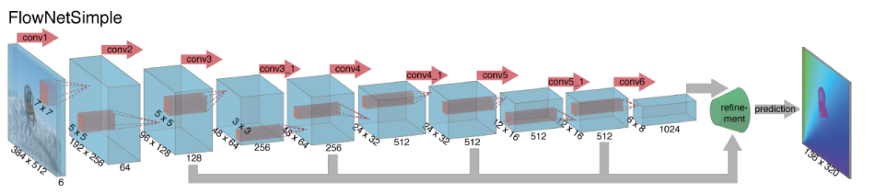
基于光流法的帧间插值


Reference