Install Cpp jupyter kernel, Image Guied Filter
Install Cpp kernel
- jupyter notebook 安装 C/C++ kernel - KEN的文章 - 知乎
conda install xeus-cling -c conda-forge- after install
jupyter kernelspec list- fix issue
-
by
cp /opt/anaconda3/envs/gpu/lib/python3.8/_sysconfigdata_x86_64_conda_cos6_linux_gnu.py /opt/anaconda3/envs/gpu/lib/python3.8/_sysconfigdata_x86_64_conda_linux_gnu.py -
check installation
python3 /opt/anaconda3/envs/gpu/share/jupyter/kernels/python3 xcpp11 /opt/anaconda3/envs/gpu/share/jupyter/kernels/xcpp11 xcpp14 /opt/anaconda3/envs/gpu/share/jupyter/kernels/xcpp14 xcpp17 /opt/anaconda3/envs/gpu/share/jupyter/kernels/xcpp17
Guided Image Filtering
Image Filtering
- Explicit LTI [linear translation-invariant, Linear time-invariant]
- Explicit Weighted-Average Filters
- Gaussian filter
- Laplacian filter
- Sobel filter
- the process of solving a Poisson Equation
- HDR compression[high dynamic range][4]
- image stitching[5]
- image matting[6]
Related
- Explicit Weighted-Average Filters
- Bilateral Filter
- 距离参数*差异参数,作为权重
-
The bilateral filter computes the filter output at a pixel as a weighted average of neighboring pixels
- 看起来像是二阶过滤?
- time cost
- brute-force, $O(Nr^2)$
- [15,16], $O(N)$
- [17]Adams et al. color image
- $r$:
kernel radius -
All the abovemethods require a high quantization degree to achieve satisfactory speed, but at the expense of quality degradation
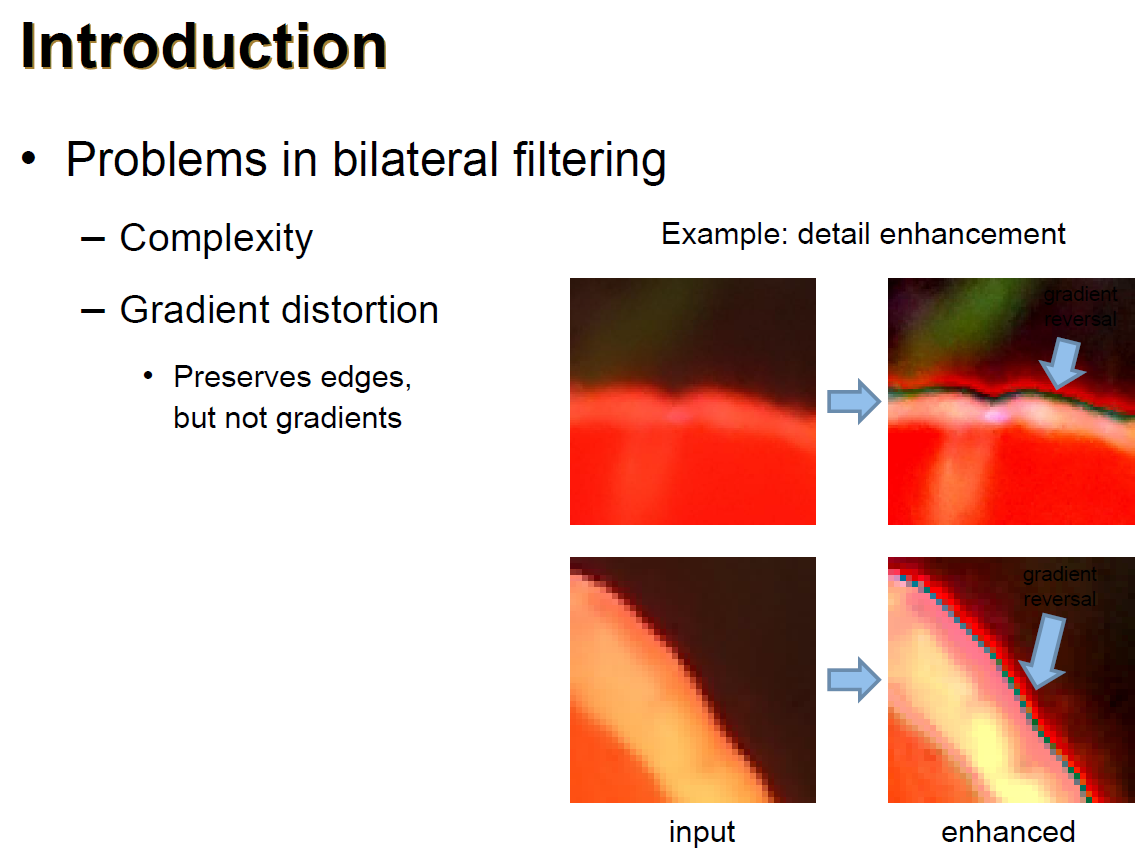
- problem
- gradient reversal
- Bilateral Filter
- Optimization-based Image Filtering
-
generate high quality results, solving the corresponding linear system is time-consuming.
-
- Nonaverage Filters, 非均质滤波, 非线性滤波
- 中值滤波
- Total-Variation filter
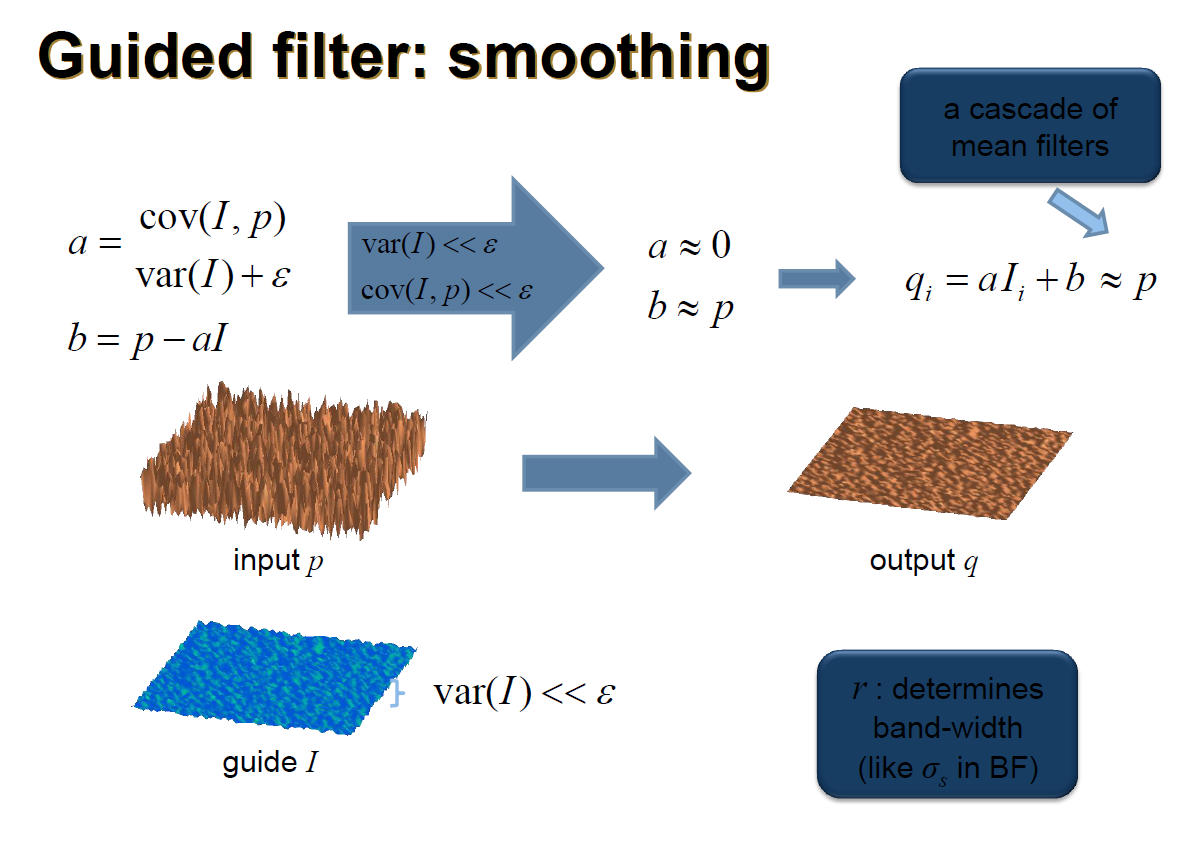
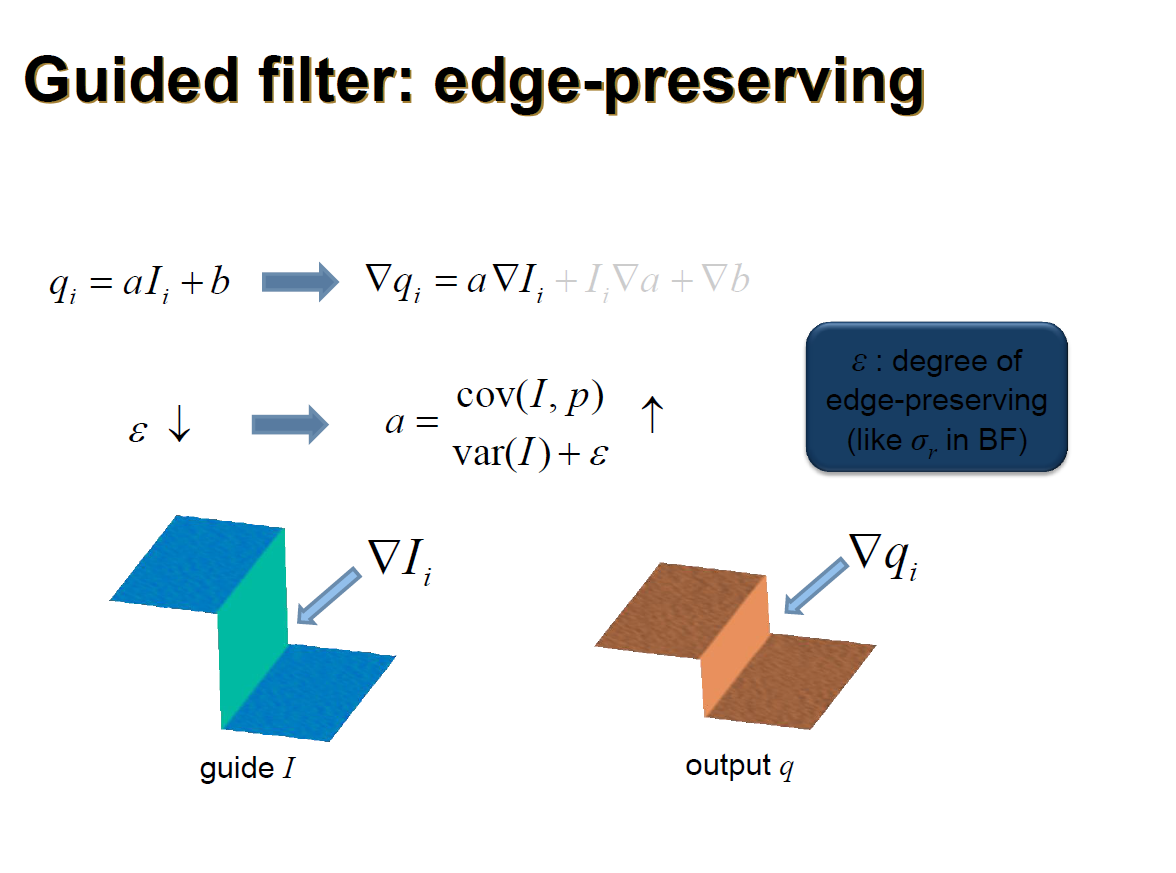
- Guided Filter
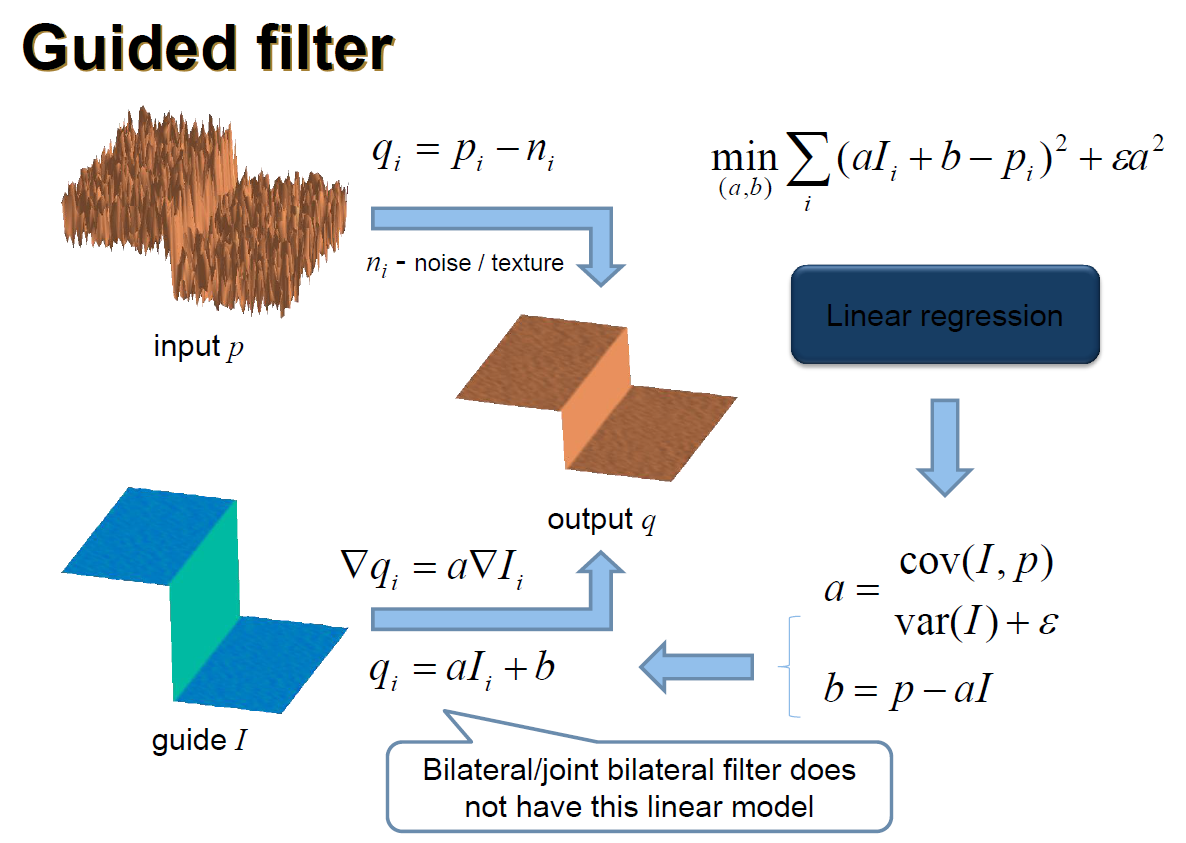
- term
- $q$: output Image
- $p$: input Image
- $I$: guide Image
- $w$: window
- $k$: the k_th windows
- $a,b$: linear model params
- $n$: noise or texture information
- principle
-
$$ \begin{aligned} q_i &= a_kI_i + b_k, \forall i \in w_k&(1)\\ q_i & = p_i - n_i&(2)\\ E(a_k,b_k) &=\sum_{i\in w_k}\big((a_k I_i + b_k - p_i)^2\big)+\epsilon a_k^2&(3)\\ a_k&=\frac{\frac{1}{\vert w\vert}\sum_{i \in w_k }I_i p_i - \mu_k\bar{p_k}}{\sigma_k^2+\epsilon}&(4)\\ b_k&=\bar{p_k}-a_k\mu_k&(5)\\ q_i&=\frac{1}{\vert w\vert}\sum_{i \in w_k }a_k I_i+b_k&(6)\\ \end{aligned} $$
- 其中
- $(1)$: 期望的引导图和输入图的线性关系
- $(2)$: 输入和输出之间差一个噪声或纹理
- $(3)$: 领回归计算$a,b$的值
- $(4,5,6)$: 参数和输出图片计算
-
- evaluation
- PSNR [Peak signal-to-noise ratio]
-
$$ \begin{aligned} PSNR&=10\log_{10}\frac{MAX_I^2}{MSE}\\ &=20\log_{10}\frac{MAX_I}{\sqrt{MSE}}\\ &=20\log_{10}MAX_I-10\log_{10}{MSE}\\ \end{aligned} $$
-
- PSNR [Peak signal-to-noise ratio]
Code
- mylikes
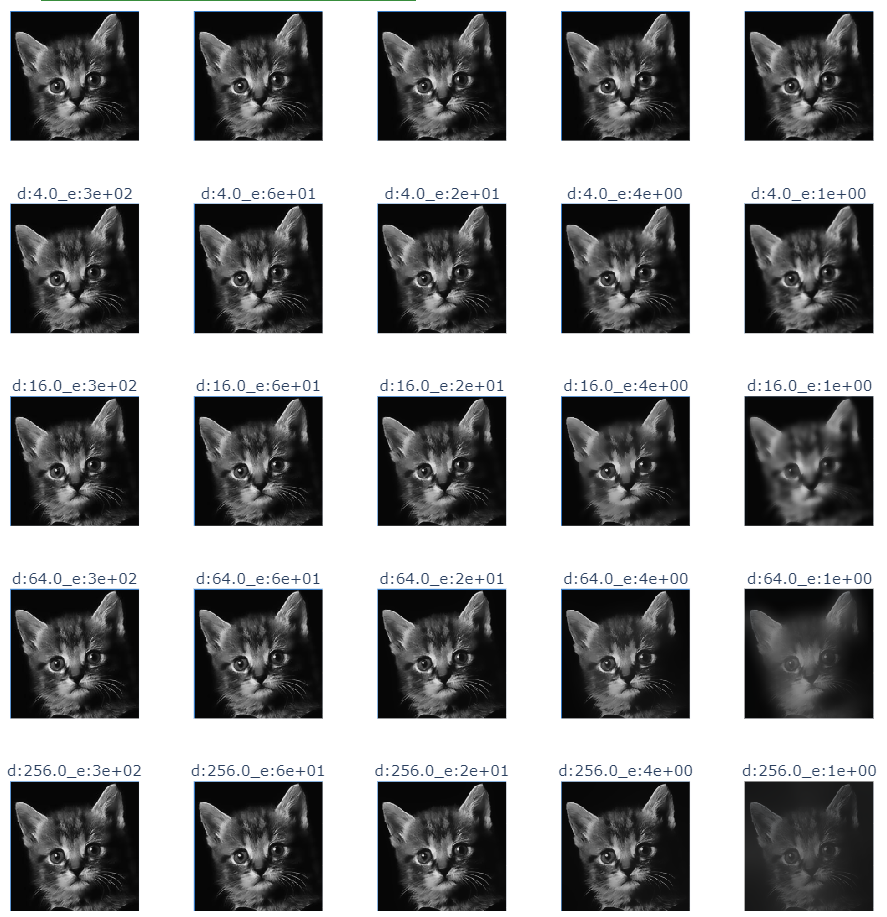
- cat guide filter
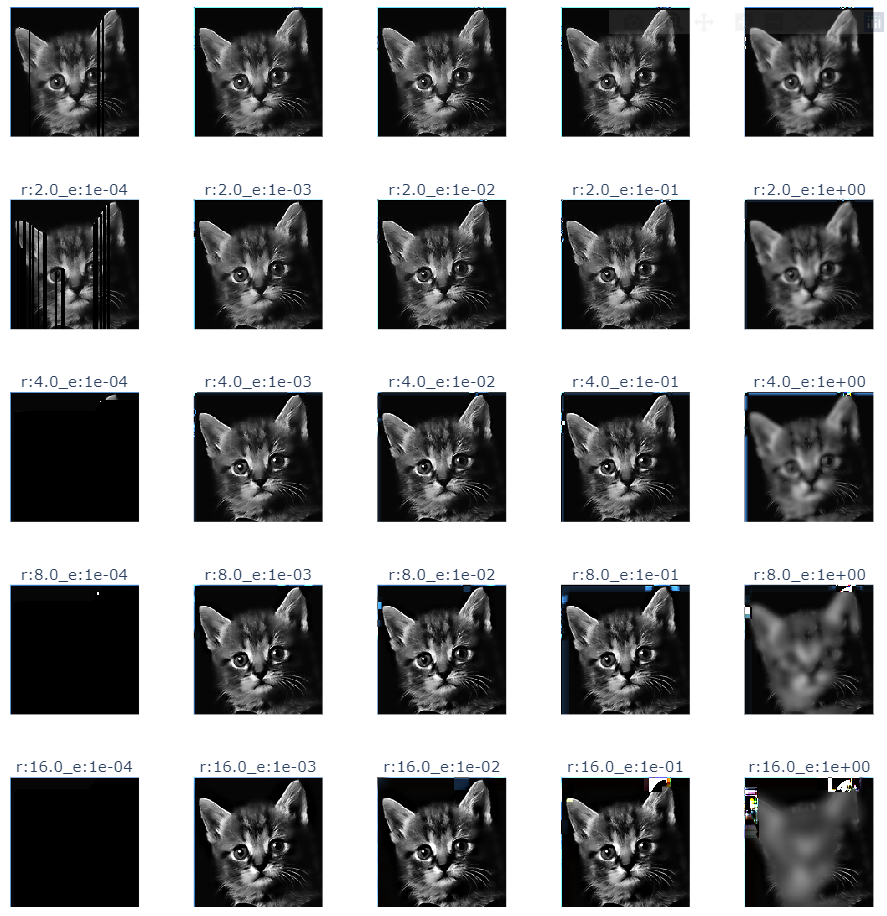 4
4
- cat bi filter
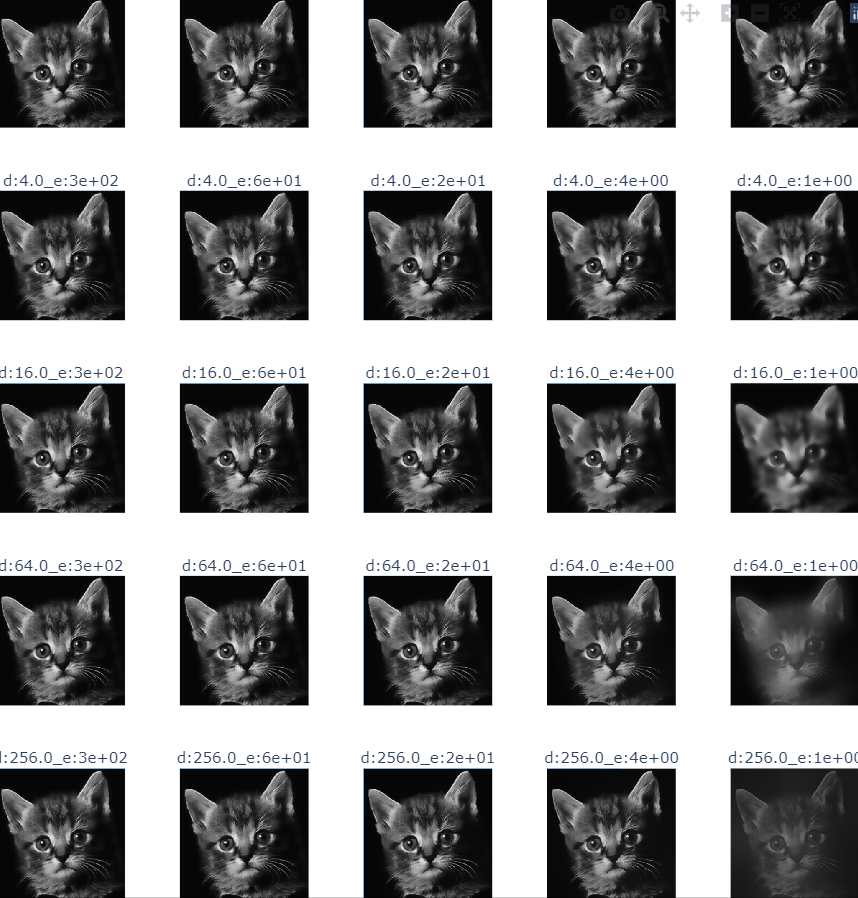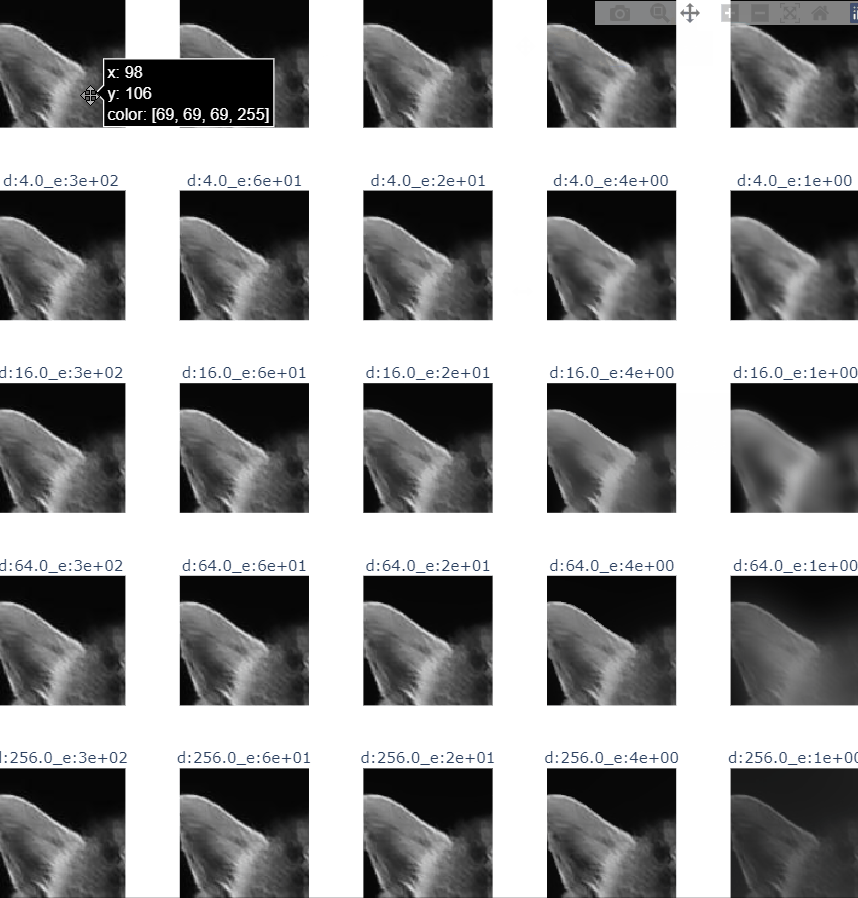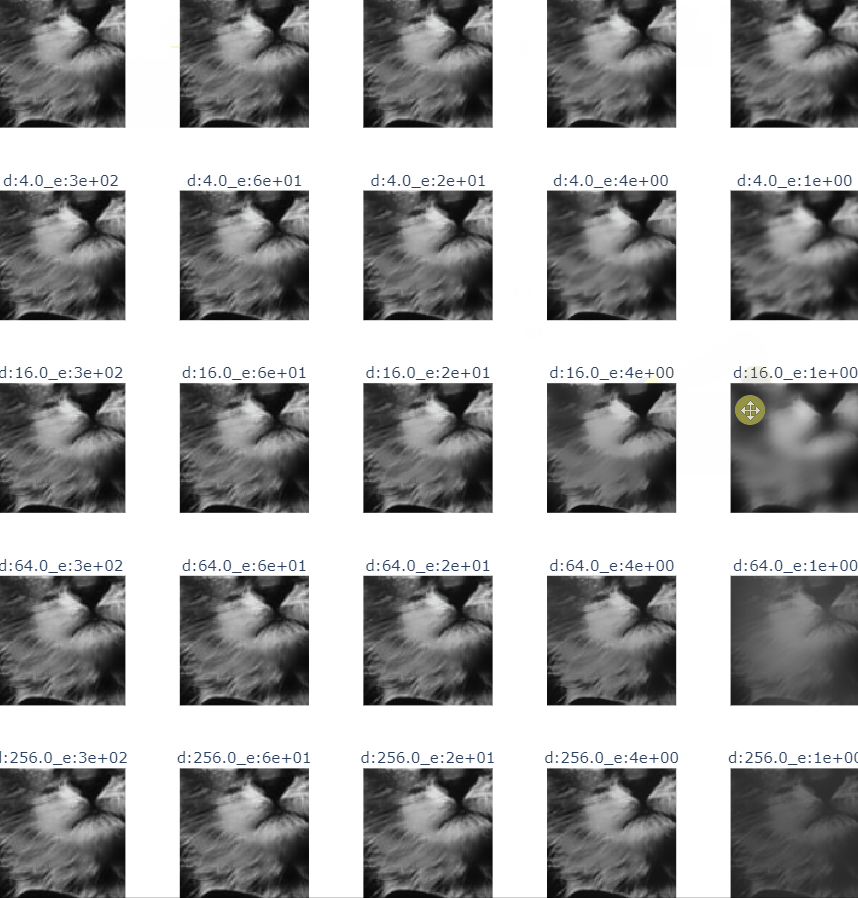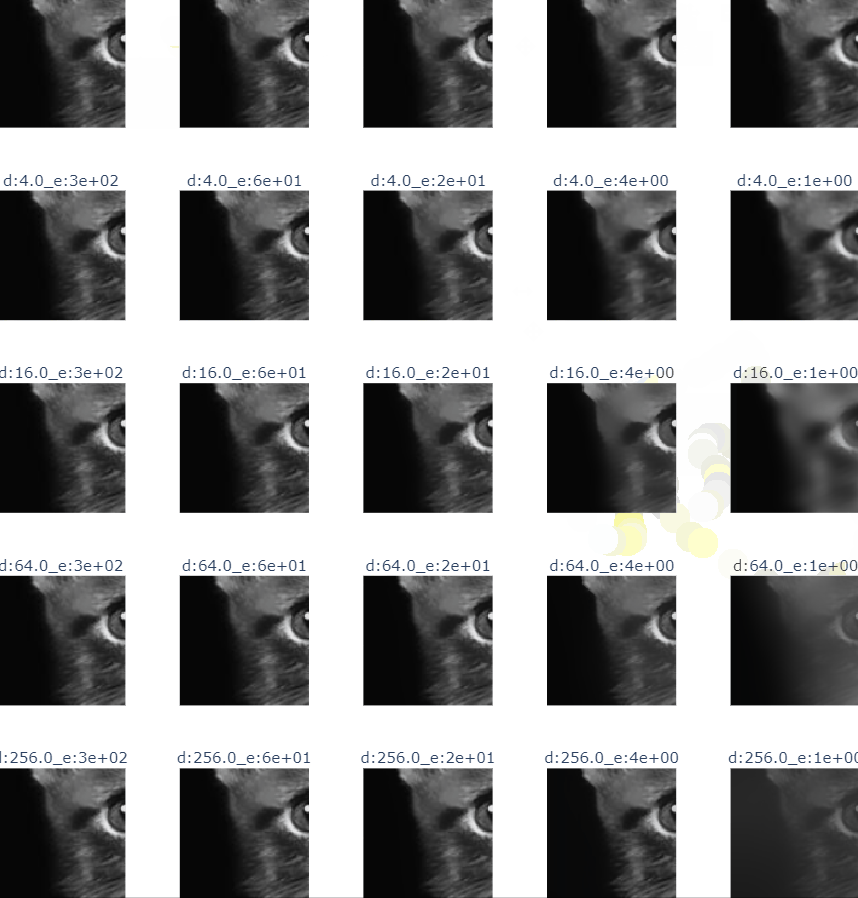
def guider_filter_image(image_name:str):
img = cv2.imread(image_name)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
radius = [2**x for x in range(5)]
epsilon = [.1**x for x in range(5)]
row = len(radius)
col = len(epsilon)
guided = []
titles = []
for p in tqdm(cartesian_product([radius, epsilon])):
r, e = p
title = f"r:{r}_e:{e:.0e}"
guided.append(guidedFilter(guide=img, src=img, radius=int(r), eps=e))
titles.append(title)
fig = px.imshow(
np.array(guided),
facet_col_wrap = col,
facet_col = 0,
)
for i, label in enumerate(titles[::-1]):
fig.layout.annotations[i]['text'] = label
fig.update_xaxes(showticklabels=False).update_yaxes(showticklabels=False)
fig.update_layout(
autosize=False,
width=720,
height=720,
margin=dict(l=0,r=0,b=0,t=0, pad=0,autoexpand=False))
fig.show()