Nerf and 3DGS
Trans-LoRA: towards data-free Transferable Parameter Efficient Finetuning
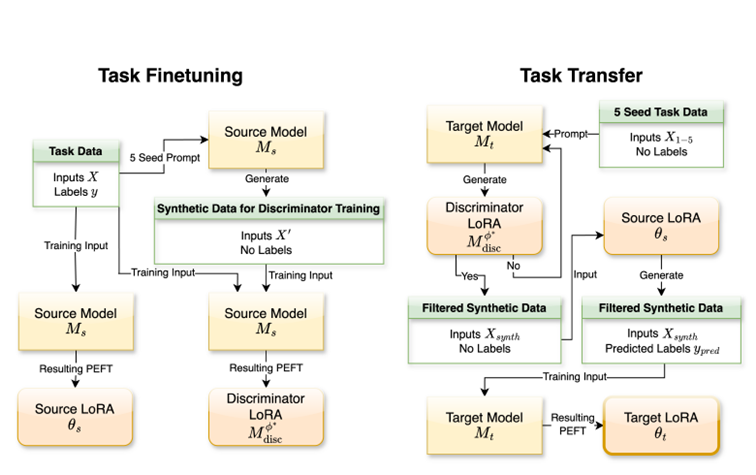
The main contributions of this method are:
- It use a Discriminator module to fit the distribution of task data to reduce data transfer.
- This training process of lora for new base model is simplified. Problems
- This method mainly focus on the transfer between Llama and Gemma. No other base model be compared.
- Not sure how long will be spent by using discriminator module to generate synthetic data.
NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis
- First of all, this paper using 5 different parameters to describe the image pixel, which could be consider as a light ray.
- And then, sample a series of points from the ray. Therefore, we could use x,y,z and theta, phi to describe the specific color from different direction, which is a kind of voxel fog.
- Through an implicit function, the output should be the color and the density.
- There is a very interesting point. The author split sigma from the last two step of network, and concat back to the network. The explanation is, the author believe that, the voxel fog should have the same density, but different color from different direction.
- Second of all, this paper out put the color and density to prepare for volume rendering, which as described in equation 1.
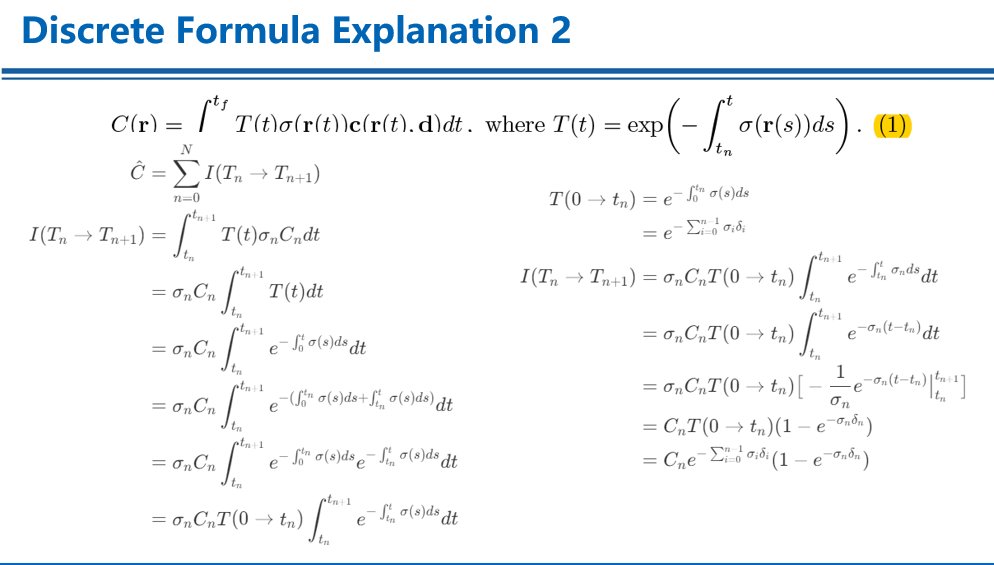
- For enhance the result quality, nerf using stratified[死dry ty fy] sampling to implement that.
- First, use 64 uniform sampling point to describe the ray curve. And then, use another 128 point to get high frequency information
- Here the fine sample point is actually from the pdf function. We could use softmax to smooth weight parameter, then get the cdf function.
- The last detail is positional encoding.
3D Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering
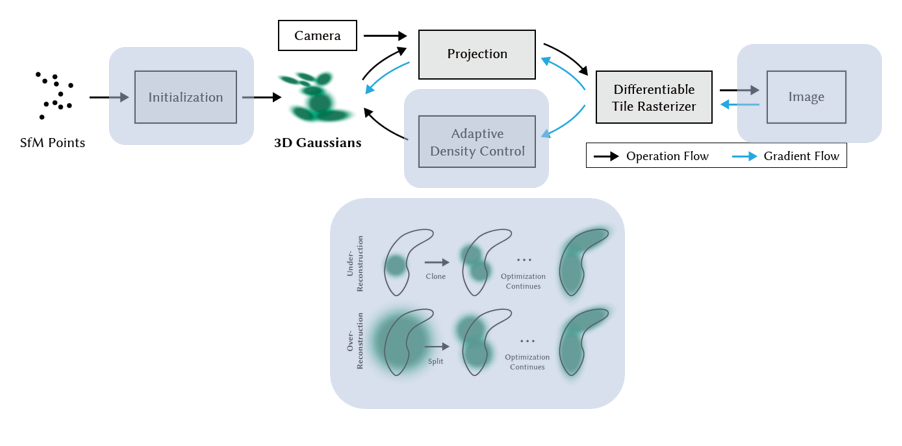
- First, GS initial the gs spherial point cloud with three cloest point by calculated with knn.
- Second, GS use some camera matrix and differentiable tile rasterization to get the 2d image.
- Third, GS use adaptive density contorl to clone or splat one or more gs sphere to fit the result.
- The loss is just MSE.
- The main contribution of this paper is, it use lots of cuda to speed up the computating process. It also implement a cuda method to rasterizer the 3dgs cloud point.
AtomGS: Atomizing Gaussian Splatting for High-Fidelity Radiance Field
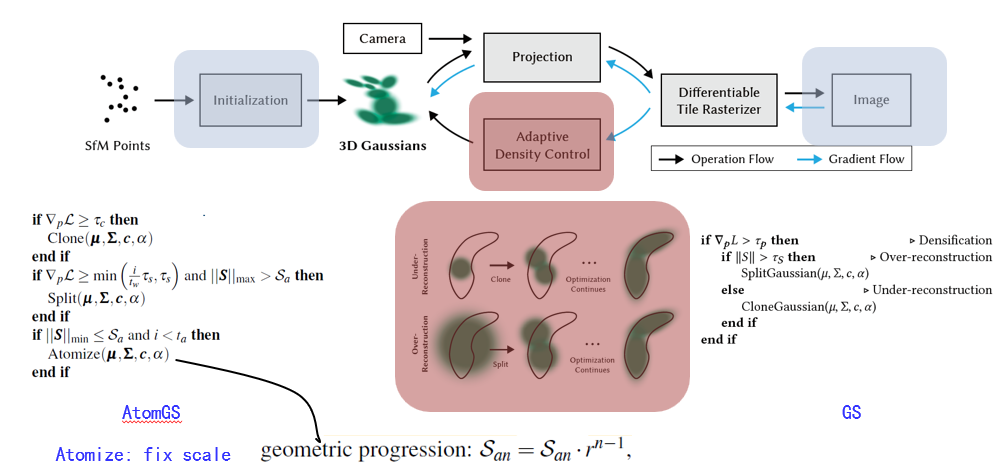
- The first point of optimization is way of Initialization.
- Not like GS, AtomGS use isotropic spheroids with a uniform size instead of anisotropic spheroids with of varying sizes.
- The author believe this will impose the priority of densifying them to accurately fill gap in the geometry.
- The second optimization is that introduce Normal Loss and Multi-scale ssim loss to control more detail.
- Here Normal Loss is calculated by multiplying curvature map and edge map with a weight function w(omega).
- The adptive density controlling has a little bit difference, AtomGS set a new threshold tau_c and tau_s to control the clone and split process.
Nerfbusters: Removing Ghostly Artifacts from Casually Captured NeRFs
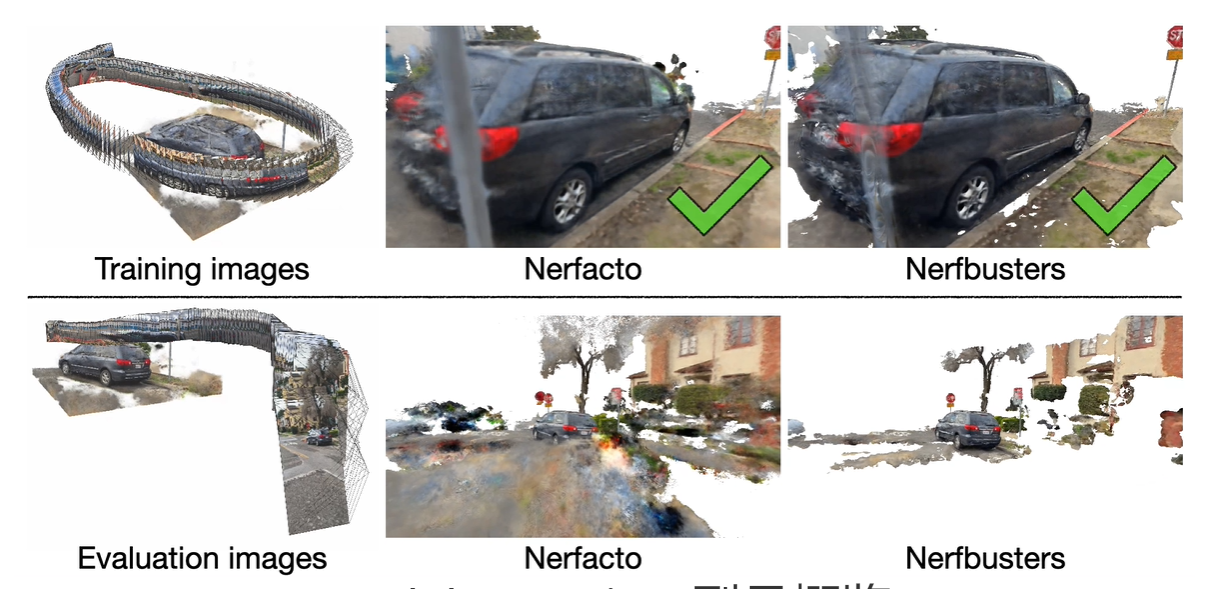

- a local 3d diffusion prior and a density socre distillation sample loss.
- use importance sampling to query cube with nerf densities.
- Computing a density score distillation sampling(DSDS) that penalize Nerf diffusion model.