FruitNeRF: A Unified Neural Radiance Field based Fruit Counting Framework
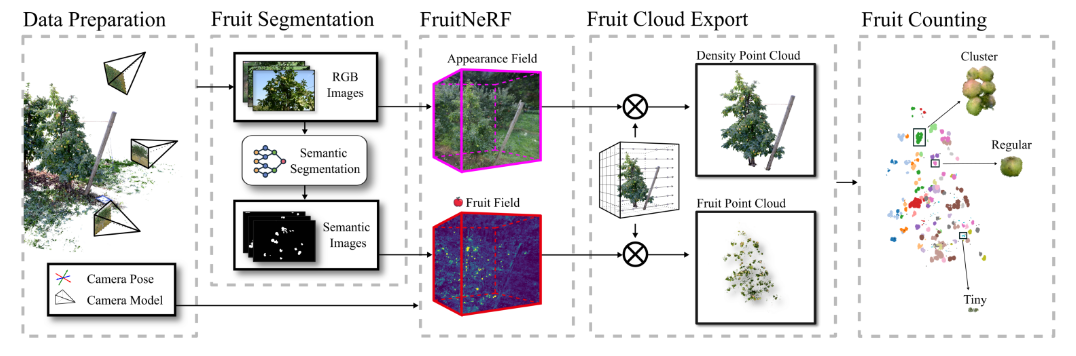
- The main idea of this paper is to use segmentation result from SAM or GroundingDINO to generate another neural radiance field to point out the fruit in 3d space. Then use the high light point to count fruit with point clusting algorithm.
- Therefore, this paper highly rely on the result from former Segment model. To do that, this author fine-tune this model and compare with the original model.
2DGS: 2D Gaussian Splatting for Geometrically Accurate Radiance Fields
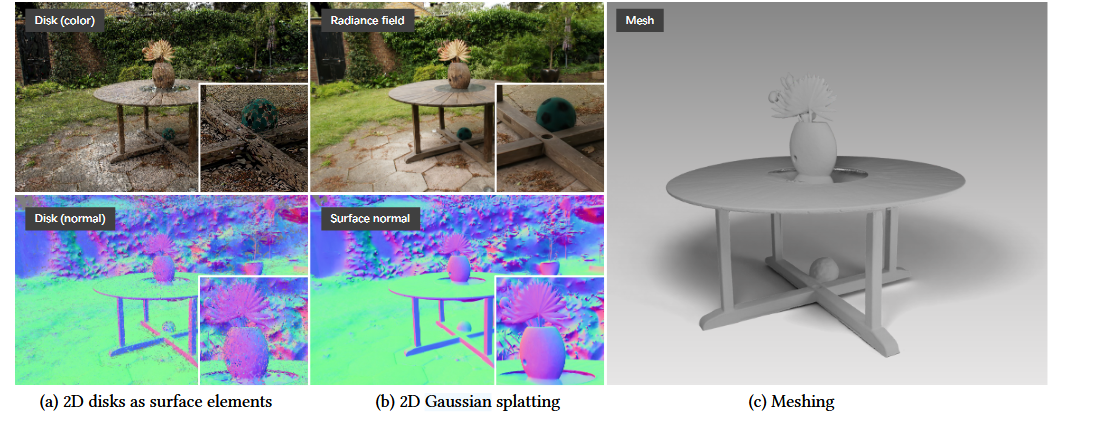

- This paper focus on fix the 3d spacial consistency problem in 3DGS. The author believe that, that issue is caused the 3DGS rendering process. The inconsistency of 3D GS sphere when the noval view change is uncontious.
- Therefore, this author try to use the 2D GS Disk to restain the rendering result from different view. Basically, 2DGS using the surfal method to replace the 3D volume rendering method to get a better result.
- However, unlike 3DGS, 2DGS is not very good at reconstructing on transparent object, such like, water and glass.
CityGaussian: Real-time High-quality Large-Scale Scene Rendering with Gaussians
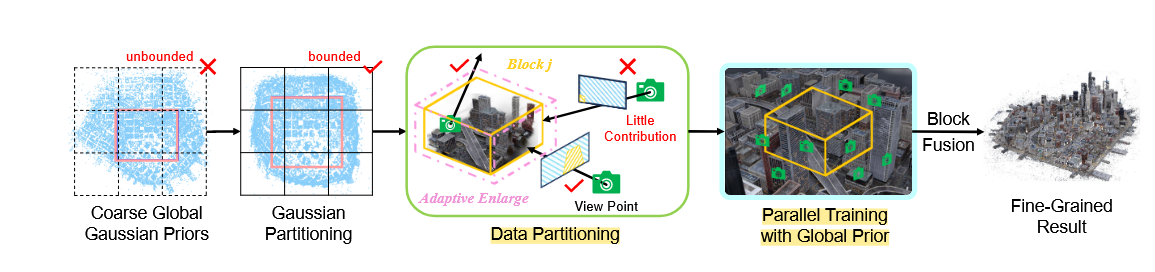
- The main strategy of this paper is to split each tile into a small space block to speed up the rendering and training process.
- There are two core contributions of this paper. First, the author use divide-and-conquer strategy and block-wise strategy to split the large-scale scene, which usually in urban reconstruction task, into several small block. For rendering process, the author use a method like volume rendering to calculate the relationship of each block from far to near from the camera.
- Second, the author try to apply a floater removing algorithm to remove the foggy artifact, which usually appear in the 3DGS result. This method is more like a statistical algorithm, called Median Absolute Deviation, I’m not very familiar with this method, not sure why the author chose this to do that.
Grounding DINO: Marrying DINO with Grounded Pre-Training for Open-Set Object Detection
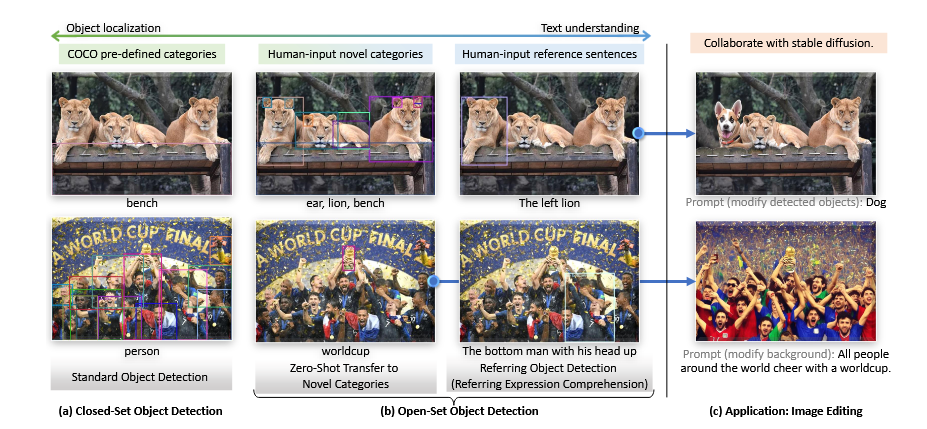
- For segmentation task, the traditional method is more for the close dataset, which means that, such method can not handle all kind of un-seen data, which is the Open-Vocabulary task.
- To do that, typically, there are two general way to solve this problem. Referring and Grounding. The former one is based on CLIP method and compare the contrastive loss between the clip predict result and the ground-truth. The latter one is based on the BERT method to minimize the contrastive loss. However, unlike the Referring method, the Grounding method put a sequence of word for a single one picture to predict the result bbox and the label.
Grounded SAM: Assembling Open-World Models for Diverse Visual Tasks

- The key idea is to combine SAM and GroundingDINO to generate a more accurate result for the fruit counting task.
- Grounded: Object Detection task
- SAM: Semantic Segmentation task
- The main pipeline is. First, use Grounded model to generate the bbox. Then feed this bbox as a prompt to SAM model to get a more accurate segmentation result.
- For auto-annotation task, we could use RAM-Grounded-SAM.
- For high controllable image editing task, we could use Grounded-SAM-SD
- For Promptable Human Motion Analysis, we could use Grounded-SAM-OSX
- To decompose task to makes the reasoning process more explainable.